
17/05/2022
U&I Logistics - With the current trend in globalization, international markets are becoming popular and expanding. Then, exploring the payment methods for international trade will help buyers and sellers in many countries easily and quickly trade.
In order for individuals and businesses to choose the most appropriate and secure method, let's review the knowledge of payment methods for international trade with U&I Logistics in this article!
A method of payment in international trade is a way for the importer to pay the exporter in international trade. There are five primary payment methods for international trade applied, typically:
In international payments, remittance is one of the most commonly used payment methods. In which, the customer side (remitter) requests the bank in their country to transfer the funds upon receiving the request of the customer.
Remittance is performed in the following order:
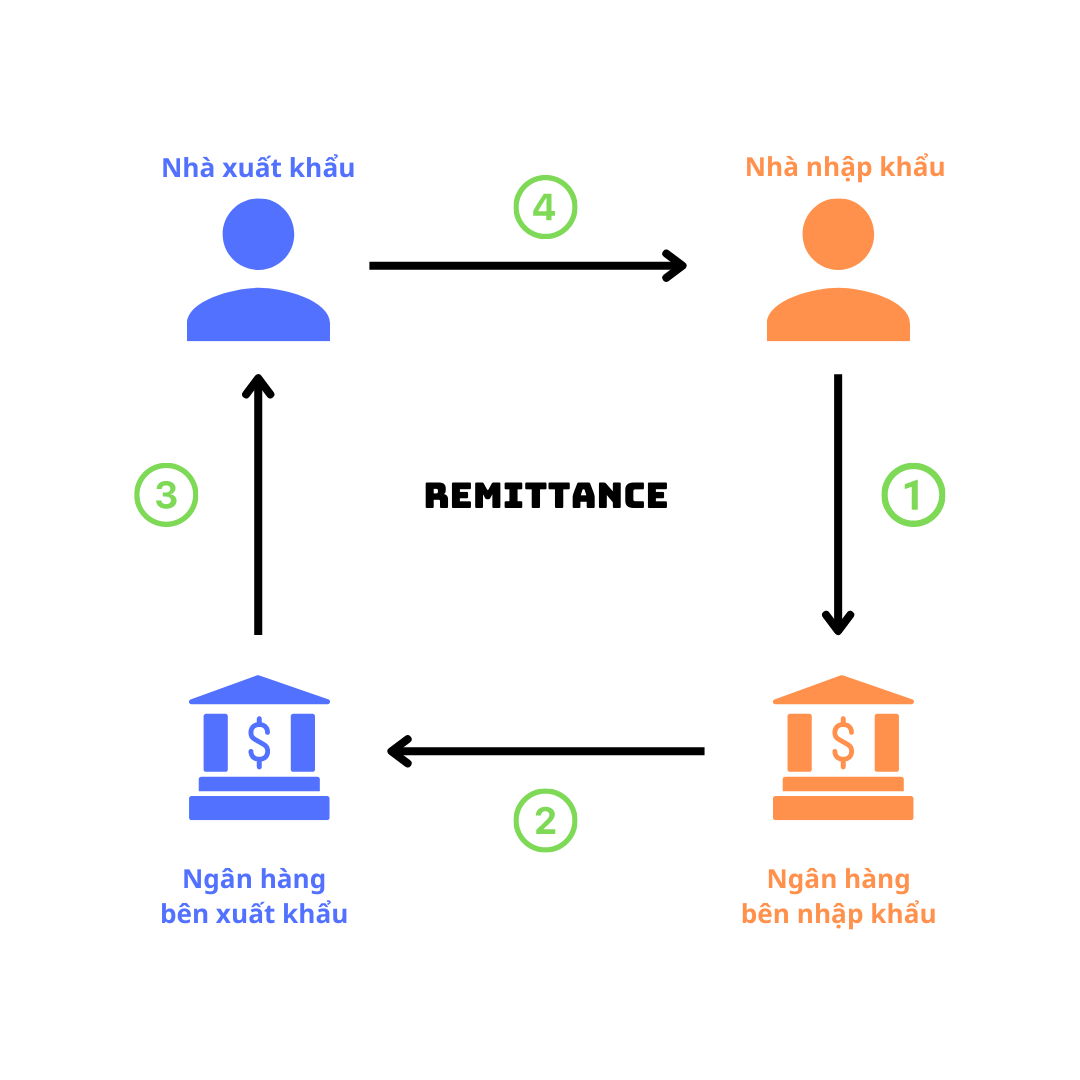
1) The importer writes a bank transfer request (money order) and sends it to the importer's bank, requesting to transfer the funds to the exporter.
2) The remittance bank requests the correspondent bank to transfer the funds to the recipient and to send a debit note to the importer.
3) The correspondent bank of the exporting country transfers the funds to the beneficiary and sends them notice.
4) The exporter delivers the goods to the importer according to the provisions of the contract.
Collection Of Payment is a payment method where the exporter, after delivering the goods to the buyer, will make a draft and send it to the collecting bank for the amount stated on the draft. There are two types of collection methods:
– Clean collection.
– Documentary collection.
Clean Collection is a payment method in which collection documents include only financial documents, not commercial documents. Such commercial documents will be sent directly to the importing party without advising through a bank.
The clean collection is performed in the following order:
.png)
1) The seller and the buyer sign an international trade contract.
2) The exporter delivers the goods to the importer with commercial documents.
3) The exporter submits the collection application with financial documents to the remitting bank.
4) The remitting bank sends the remitting order and financial documents to the collecting bank.
5) The remitting bank reviews the documents and sends a remitting notice to the importer.
6) Importer sends the funds and documents to the remitting bank.
7) The collecting bank transfers the funds to the remitting bank.
8) The remitting bank transfers the funds to the exporter's account.
Documentary Collection is the method by which the exporter's bank performs the service of collecting sales proceeds from the importer to the exporter, on the basis of a set of delivery documents.
There are two types of documentary collection:
- Documentary Against Payment – D/P.
- Documentary Against Acceptance – D/A.
The documentary collection is performed in the following order:
.png)
(1) The exporter and the importer enter into an international sale and purchase contract.
(2) The exporter delivers the goods to the buyer.
(3) The seller fills out a collection request form with documents (bank's form) and sends it with the financial and commercial documents, authorizing the remitting bank to collect the goods from the importer.
(4) The remitting bank makes a collection order and sends the same set of documents to the collecting bank.
(5) The collecting bank notifies the collection order and presents the documents to the importer for payment or acceptance.
(6) The importer pays, signs for payment, or draws promissory notes/receipts.
(7) The collecting bank hands over the commercial documents for the buyer to pick up the goods.
(8) The collecting bank transfers the collected money to the remitting bank.
(9) The collecting bank credits the seller's account, or returns to the seller the signed financial documents for payment, or other financial documents drawn by the buyer.
Open account is an international payment method, in which the exporter, after completing the delivery of goods, debits the account of the importer in a monitoring book and the payment of these debts is made periodically as agreed upon.
The documentary collection is performed in the following order:
.png)
(1) The exporter delivers the goods and documents to the importer.
(2) The exporter sends a debit note to the importer.
(3) The importer carries out procedures to transfer the funds to the seller.
(4) The importing bank transfers the funds to the exporting bank.
(5) The bank advises the exporter.
Letter of Credit – L/C is a letter issued by the bank at the request of the importer, promising to the seller to pay a specific amount within a certain period of time if the exporter can present a set of valid documents in accordance with the provisions of the L/C. L/C is briefly understood as a letter of commitment from the bank to pay the exporter.
Letter of Credit is performed in the following order:
.png)
(1) The importer makes an application for a letter of credit and sends it to his bank, requesting a letter of credit for the exporter.
(2) Based on the application, the bank opening the L/C will draw up a letter of credit and, through its correspondent bank in the exporting country, notify the opening of the letter of credit and forward the letter of credit to exporters.
(3) After receiving this notice, the advising bank will notify the exporter of the entire notice of opening the letter of credit, upon receipt of the original letter of credit, immediately forward it to the exporter.
(4) If the exporter accepts the letter of credit, the goods will be delivered, if not, the bank is requested to open the L/C to amend the letter of credit in conformity with the contract
(5) After delivery, the exporter prepares the documents required by the letter of credit, advises it through the bank, and notifies the bank opening the L/C to proceed with the payment.
(6) The bank opening the L/C checks the documents, if it is in compliance with the letter of credit, then proceeds the payment. If the reconciliation does not match, the bank will refuse to pay and return all documents to the exporter.
(7) The bank opening the L/C demands the funds from the importer and sends the documents to the importer after receiving the funds or accepting payment.
(8) The importer re-checks the documents, if found to be in compliance with the letter of credit, then refunds to the bank opening the letter of credit, if not, has the right to refuse to pay.
Cash Against Documents - CAD is a method where the importer requests the bank to open a Trust Account to pay the exporter when the exporter presents the required set of documents. After completing the delivery obligation, the exporter will present a set of documents to the bank to enter the payment.
Cash Against Documents is performed in the following order:
.png)
1) After signing a contract with the Exporter (where the prescribed payment method is CAD), the importer needs to request the service. The importer and the bank will sign a Memorandum of Understanding (Memorandum), containing the following contents:
After the importer transfers the full amount of deposit, a Trust Account will be opened to record the deposit, and the Bank will also notify the exporter that the Trust Account is active
2) After checking the conditions of the Trust Account, if accepted, the exporter delivers the goods to the carrier for delivery to the place requested by the importer.
3) The exporter, after delivering the goods, presents the documents required by the Memorandum at the Bank.
4) After collecting the banking service fee as directed in the Memorandum of Understanding, the bank will review and compare the documents as required by the Memorandum of Understanding, if appropriate, credit the exporter and debit the escrow account for the importer.
5) The bank delivers the documents back to the importer.
3. Ways to mitigate international payment risks
In the process of making international payment, if the principles are not properly applied, multiple risks will be faced. Here, U&I Logistics will share some tips to minimize the worst cases complexity in the process of making international payments.
- Choose the right payment service provider: choose banks with extensive experience in conducting international payment transactions. Most of these banks will have a team of staff with extensive professional knowledge and expertise to advise on appropriate payment methods or offer the best solutions to businesses. if unlucky. The import-export process will take place effectively and minimize losses as much as possible.
- Choose the right customer: truly understand the customers in the importing country including their financial capacity, production and business process, and consult the bank about the partner's business process. These are important things to mitigate risks, avoid encountering "virtual customers" with unclear information.
- Master the profession: improve knowledge and foreign language skills for employees in charge of import and export positions. Actively learn about legal regulations related to import and export in major markets to select appropriate countermeasures..
In light of the above article, U&I Logistics has shared with you important information about international payment methods. Hopefully, you will be able to broaden their knowledge of business operations and choose the payment methods that best suit your business.
U&I Logistics